| V:
Abbreviation for Volt. A unit
of electrical force or potential, equal to the force that will
cause a current of one Amp to flow through a conductor with a
resistance of one Ohm. |
| VAC:
Abbreviation for Volts, AC.
Voltage using alternating current. |
| VCSEL:
See vertical
cavity surface-emitting laser. |
| VDC:
Abbreviation for Volts, DC.
Voltage using direct current. |
| VDSL:
Abbreviation for very high data rate
digital subscriber line. A DSL operating at a data rate higher
than that of HDSL.
See also DSL. |
|
Vector
Quantization
(VQ):
A digital video compression
technique based on Shannons distortion-rate theory which
states that the performance of data compression systems
improves if blocks of data are coded, with larger coded data
blocks giving better performance.
|
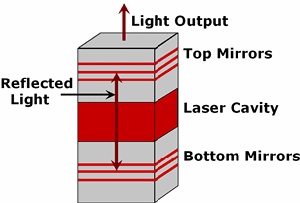
| Vertical
Cavity Surface-emitting Laser:
Lasers
that emit light perpendicular to the plane of the wafer they
are grown on. They have very small dimensions compared to
conventional lasers and are very efficient. |
|
| Vestigial-sideband
(VSB) Transmission:
A
modified double-sideband transmission in which one sideband,
the carrier, and only a portion of the other sideband are
transmitted. See also sideband. |
| VGA:
Abbreviation for video graphics
array. A high-resolution color standard for computer monitors. |
| VHF:
Abbreviation for very high frequency. The frequencies, ranging
from 30 MHz to 300 MHz, in the electromagnetic
spectrum.
Contains off-air television channels 2-12. |
| Video
on Demand (VOD):
A term used for interactive or customized video delivery
service. |
| Videoconferencing:
Conducting conferences via a video telecommunications system. |

|
| Videophone:
A telephone-like service with a picture as well as sound. |
|
Virtual
Circuit (VC): A
communications arrangement in which data from a source user
may be passed to a destination user over various real circuit
configurations during a single period of communication,
usually on a per call basis, although permanent connections
can be established.
|
| Visible
Light:
Electromagnetic
radiation
visible to the human eye; wavelengths of 400-700 nm. |
| VOD:
See video
on demand. |
| Voice
Circuit:
A circuit capable of carrying one telephone conversation or
its equivalent; the standard sub-unit in which
telecommunication capacity is counted. The U.S. analog
equivalent is 4 kHz. The digital equivalent is 64 kb/s in
North America and in Europe. |
| VPN:
Abbreviation for virtual private
network. A protected information-system link utilizing
tunneling, security controls, and end-point address
translation giving the end user the impression that a
dedicated line exists between nodes. |
| VSB:
See vestigial-sideband
transmission. |