|
ECL:
Abbreviation for emitter-coupled logic. A
high-speed logic family capable of GHz rates.
|
|
EDFA:
See Erbium-doped fiber amplifier.
|
|
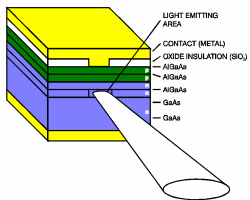
Edge-emitting Diode:
An LED
that emits light from its edge, producing more directional output than
surface-emitting LED's
that emit from their top surface.
|
|
|
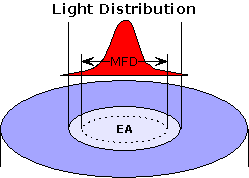
Effective Area: Light
is not distributed in the fiber core uniformly. Rather, it follows a
distribution that typically peaks in the center of the core and then
tails off near the core-cladding interface. It usually extends some
short distance into the cladding as well. (See
evanescent wave.)
Note:
For a Gaussian power distribution in a
single-mode optical fiber,
the
mode field diameter
(MFD) is that at which the light intensity is reduced to 1/e of its
maximum value.
The effective area is the area defined by the MFD.
|
|
|
EGA:
Abbreviation for enhanced graphics adapter. A medium-resolution color
standard for computer monitors.
|
|
EIA:
Abbreviation for Electronic Industries Association. An organization that
sets video and audio standards.
|
http://www.eia.org/ |
|
EMI (Electromagnetic Interference):
Any
electrical or electromagnetic interference that causes undesirable
response, degradation, or failure in electronic equipment.
Optical fibers
neither emit nor receive EMI.
|
|
EMP (Electromagnetic
Pulse):
A burst of
electromagnetic radiation that creates electric and magnetic fields that
may couple with electrical/electronic systems to produce damaging
current and voltage surges.
|
|
EMR (Electromagnetic Radiation):
Radiation made up of oscillating electric and magnetic fields and
propagated with the speed of light. Includes gamma radiation, X-rays,
ultraviolet, visible, and infrared radiation, and radar and radio waves.
|
|
Electromagnetic Spectrum:
The
range of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation from zero to infinity.
|
(Click to
Enlarge)
|
|
ELED:
See edge-emitting diode.
|
|
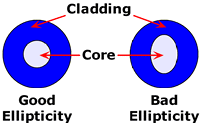
Ellipticity:
Describes the fact that the core
or cladding
may be elliptical rather than circular.
|
|
|
EM:
Abbreviation for electromagnetic.
|
|
Endoscope:
A fiber optic
bundle used for imaging and viewing inside the human body.
|
|
E/O:
Abbreviation for electrical-to-optical converter. A device that converts
electrical signals to optical signals, such as a laser diode.
|

|
|
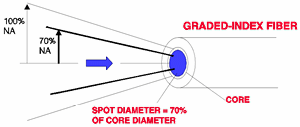
Equilibrium Mode
Distribution
(EMD):
The steady modal state of a multimode
fiber in
which the relative power distribution among modes is independent of
fiber length.
|
|
|
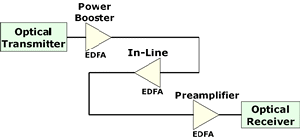
Erbium-doped Fiber Amplifier
(EDFA):
Optical fibers doped with the rare earth element, erbium, which can
amplify light in the 1550 nm region when pumped by an external light
source.
|
|
| Error Correction:
In digital transmission systems, a scheme that adds overhead to the data
to permit a certain level of errors to be detected and corrected. |
| Error Detection:
Checking for errors in data transmission. A calculation based on the
data being sent; the results of the calculation are sent along with the
data. The receiver
then performs the same calculation and compares its results with those
sent. If the receiver detects an error, it can be corrected, or it can
simply be reported. |
|
ESCON:
Abbreviation for enterprise systems connection. A
duplex
optical connector used for computer-to-computer data exchange.
|
|
|
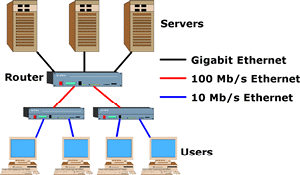
Ethernet:
A standard protocol (IEEE
802.3) for
a 10-Mb/s baseband
local area network (LAN)
bus using carrier sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD)
as the access method. Ethernet is a standard for using various
transmission media, such as coaxial cables, unshielded twisted pairs,
and optical fibers. |
|
|
Evanescent Wave:
Light guided in the inner part of an optical fiber's cladding
rather than in the core,
i.e., the portion of the light wave in the core that penetrates into the
cladding.
|

|
|
Excess Loss:
In a
fiber optic coupler,
the optical loss from that portion of light that does not emerge from
the nominal operation ports of the device.
|
|
External Modulation:
Modulation of a light source by an external device that acts like an
electronic shutter.
|
|
Extinction Ratio:
The
ratio of the low, or OFF optical power level (PL) to the
high, or ON optical power level (PH):
|
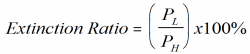
|
|
Extrinsic Loss:
In a
fiber
interconnection, that portion of loss not intrinsic to the fiber but
related to imperfect joining of a
connector
or splice.
|
|
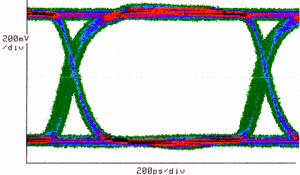
Eye Diagram:
A
diagram that shows the proper function of a digital system. The
"openness" of the eye relates to the BER
that can be achieved.
|
|