|
n:
Abbreviation for nano. One billionth or 10-9.
|
|
N:
Abbreviation for Newtons. Measure of force
generally used to specify
fiber optic cable
tensile strength. |
|
nA:
Abbreviation for nanoamp. One billionth of an Amp or 10-9
Amps. |
|
NA: See numerical aperture.
|
| NAB:
Abbreviation for National Association of Broadcasters. A trade association that promotes
and protects the interests of radio and television broadcasters before
Congress, federal agencies and the Courts. |
http://www.nab.org/ |
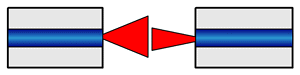
| NA Mismatch
Loss:
The loss of power at a joint that occurs when the transmitting half has
a numerical aperture greater than the NA of the receiving half. The loss
occurs when coupling light from a source
to fiber,
from fiber to fiber, or from fiber to detector.
|
|
|
National Electric Code®
(NEC):
A standard governing the use of electrical wire, cable
and fixtures installed in buildings; developed by the American National
Standards Institute (ANSI), sponsored by the National Fire Protection
Association (NFPA), identified by the description ANSI/NFPA 70-1990. |
http://www.ansi.org/ |
| NCTA:
Abbreviation for National Cable Television
Association. The major trade association for the cable television
industry. |
http://www.ncta.com/ |
|
NDSF: See
non dispersion-shifted fiber.
|
| Near-end Crosstalk
(NEXT, RN): The optical power reflected
from one or more input ports, back to another input port. Also known as
isolation directivity. |
| Near Infrared:
The
part of the infrared near the visible spectrum, typically 700 nm to 1500
nm or 2000 nm; it is not rigidly defined. |
| NEMA:
Abbreviation for National Electrical Manufacturers Association. Organization
responsible for the standardization of electrical equipment, enabling
consumers to select from a range of safe, effective, and compatible
electrical products. |
http://www.nema.org/ |
|
NEP: See
noise equivalent power.
|
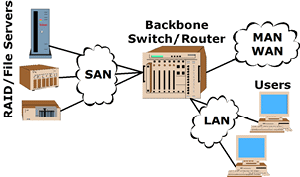
| Network:
1) An interconnection of three or more
communicating entities and (usually) one or more nodes (illustrated). 2)
A combination of
passive or
active
electronic components that serves a given purpose. |
|
|
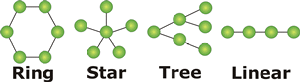
Network Topology: The specific physical, i.e.,
real, logical, or virtual, arrangement of the elements of a network.
Common network topologies include a bus (or linear) topology, a ring
topology, and a hybrid topology, which can be a combination of any two
or more network topologies. Illustrated to the right are four common
Network Topologies.. |
|
|
NF: See noise figure.
|
| NFPA:
Abbreviation for National Fire Protection Association. Publisher of the
National Electrical Code®, and 300 other codes and standards through a
full, open-consensus process. |
http://www.nfpa.org/Home/index.asp |
|
nm:
Abbreviation for nanometer. One billionth of a meter or 10-9
meters. |
| Node:
1) A terminal of any branch in network topology or an interconnection
common to two or more branches in a network. 2) One of the switches
forming the network backbone in a switch network. 3) A point in a
standing or stationary wave at which the amplitude is a minimum. |
|
Noise:
1) An undesired
disturbance within the frequency band of interest; the summation of
unwanted or disturbing energy introduced into a communications system
from man-made and natural sources. 2) A disturbance that affects a
signal and that may distort the information carried by the signal. 3)
Random variations of one or more characteristics of any entity such as
voltage, current, or data.
|
|
Noise Equivalent Power
(NEP):
The noise of optical
receivers,
or of an entire transmission system, is often expressed in terms of
noise equivalent optical power. |
|
Noise Figure (NF):
The ratio of the output
signal-to-noise ratio
to the input signal-to-noise ratio for a given element in a transmission
system. Used for optical and electrical components. |
|
Non Dispersion-shifted Fiber (NDSF):
The most popular type of
single-mode fiber
deployed. It is designed to have a
zero-dispersion wavelength
near 1310 nm. |
|
Nonlinearity:
The deviation from linearity
in an electronic circuit, an electro-optic device or a fiber
that generates undesired components in a signal. Examples of fiber
nonlinearities include SBS,
SRS,
FWM,
SPM,
XPM,
and
Intermodulation.
|
|
Non Zero-dispersion-shifted Fiber (NZ-DSF):
A
dispersion-shifted single-mode fiber
that has the
zero-dispersion wavelength
near the 1550 nm window, but outside the window actually used to
transmit signals. This strategy maximizes bandwidth while minimizing
fiber nonlinearities. |
|
NRZ:
Abbreviation for non-return to zero. A common
means of encoding data that has two states termed “zero” and “one” and
no neutral or rest position. |
|
ns:
Abbreviation for nanosecond. One billionth of a
second or 10-9 seconds. |
|
NTSC:
1) Abbreviation for National Television Systems Committee. The
organization which formulated the NTSC system. 2) Standard used in the
U.S. that delivers 525 lines at 60 frames per second. |
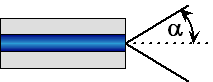
| Numerical
Aperture
(NA):
The light-gathering ability of a fiber;
the maximum angle to the fiber axis
at which light will be accepted and propagated through the fiber. NA =
sin
a, where a is the
acceptance angle.
NA also describes the angular spread of light from a central axis, as in
exiting a fiber, emitting from a
source,
or entering a detector.
|
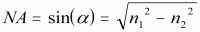
|
|
nW:
Abbreviation for nanowatt. One billionth of a Watt or 10-9
Watts. |
| Nyquist Frequency:
The lowest sampling frequency that can be used for
analog-to-digital conversion
of a signal without resulting in significant aliasing. Normally, this
frequency is twice the rate of the highest frequency contained in the
signal being sampled. Also called Nyquist rate.
|
| NZ-DSF:
See non zero-dispersion-shifted fiber. |