| s:
Abbreviation for second. |
| Sampling
Rate:
The number of discrete sample measurements made in a given
period of time. Often expressed in megahertz
(MHz) for video. |
| SAP
(Secondary Audio Programming):
Secondary audio signal that is broadcast along with a
television signal and its primary audio. SAP may be enabled
through either the television, stereo VCR equipped to receive
SAP signals, or an SAP receiver. SAPs may be used for a
variety of enhanced programming, including providing a
"video description" of a program's key visual
elements, inserted in natural pauses, that describes actions
not otherwise reflected in the dialog, used by visually
impaired viewers. This service also allows television stations
to broadcast programs in a language other than English, and
may be used to receiver weather information, or other forms of
"real-time" information. |
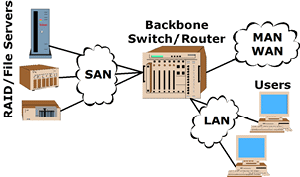
| SAN
(Storage Area Network):
Connects a group of computers to high-capacity storage
devices. May be incorporated into local
area networks (LAN),
metropolitan
area networks (MAN),
and wide
area networks (WAN). |
|
| Saturation:
1) In a communications system, the condition in which a
component of the system has reached its maximum traffic
handling capacity. 2) The point at which the output of a linear
device,
such as a linear amplifier, deviates significantly from being
a linear function of the input when the input signal is
increased. 3) The degree of the chroma or purity of a color. |
| S-Band:
The wavelength region between 1485 nm and 1520 nm used in some
CWDM
and DWDM
applications. |
| SBS:
See stimulated
Brillouin scattering. |
| SC:
Abbreviation for subscription channel connector. A
push-pull type of optical connector
that features high packing density, low loss, low backreflection,
and low cost. |
|
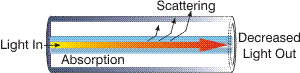
| Scattering:
The change of direction of light rays or photons after
striking small particles. It may also be regarded as the
diffusion of a light
beam caused by the inhomogeneity of the transmitting material. |
|
| Scalable
Coding:
The ability to encode a visual sequence so as to enable the
decoding of the digital data stream at various spatial and/or
temporal resolutions. |
| Scalable
Video:
Refers to video compression that can handle a range of bandwidths,
scaling smoothly over them. |
| Scanning:
1) In telecommunications systems, periodic examination of
traffic activity to determine whether further processing is
required. 2) In television, facsimile, and picture
transmission, the process of successively analyzing the colors
and densities of the object according to a predetermined
pattern. |
S-CDMA:
A proprietary version of code division multiple access (CDMA).
S-CDMA was developed by Terayon Corporation for data
transmission across coaxial cable networks. S-CDMA scatters
digital data up and down a wide frequency band and allows
multiple subscribers connected to the network to transmit and
receive concurrently. This method of data transmission was
developed to be secure and extremely resistant to noise.
|
| SCM:
Abbreviation for subcarrier multiplexing.
The process by which multiple subcarrier signals are combined
onto one signal. |
| Scrambler:
1) A device that transposes or inverts signals or otherwise
encodes a message at the transmitter
to make the message unintelligible at a receiver
not equipped with an appropriately set descrambling device.
Scramblers usually use a fixed algorithm or mechanism. 2) A
device intended to normalize the duty cycle of a data stream
to be close to 50%. |
| Scrambling:
To transpose or invert digital
data according to a prearranged scheme in order to break up
the low-frequency patterns associated with serial digital
signals. |
| SCSI:
Acronym for small computer system interface. An intelligent
interface device that expands a microprocessor (CPU) bus to
facilitate connections to multiple peripherals (e.g., CD-ROM
drives, hard drives, or scanners) and exchange data with those
peripherals via a separate communications bus. |
| SDTV:
Abbreviation for standard-definition television. Synonym NTSC
television transmission. |
| SECAM:
Abbreviation for Système Électronique
Couleur avec Mèmoire. A TV standard used in various parts of
the world. Delivers 625 lines at 50 frames per second. |
| Selfoc
Lens:
A trade name used by the Nippon Sheet Glass (NSG) Company for
a graded-index
fiber
(GRIN) lens; a lens that uses refractive index gradients to
focus light. |
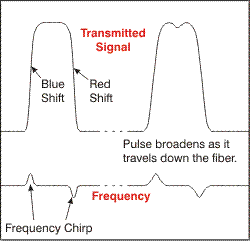
| Self-phase
modulation (SPM):
A fiber nonlinearity
caused by the nonlinear index
of refraction
of glass. The index of refraction varies with optical power
level causing a frequency chirp
which interacts with the fiber’s dispersion
to broaden the pulse. |
|
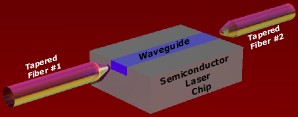
| Semiconductor
Optical Amplifier (SOA):
A laser
diode
without end mirrors coupled to the fibers
on both ends. Light coming in either fiber is amplified by a
single pass through the laser diode. An alternative to EDFAs. |
|
| Sensitivity:
See receiver
sensitivity. |
| Serial:
One bit at a time, along a single transmission path. |
| Serial
Digital:
Digital information that is transmitted in serial form. Often
used informally to refer to serial digital television signals. |
| Serial
Digital Interface (SDI):
A 10-bit, scrambled, polarity independent interface, based on
a 270 Mb/s data rate, with common scrambling
for both component ITU-R 601, composite digital video, and
four channels of (embedded) digital audio. Most new broadcast
digital equipment includes SDI. |
| Serial
Digital Transport Interface (SDTI):
Another name for SMPTE
305M. Allows faster-than-real-time transfers between various
servers and between acquisition tapes, disk-based editing
systems and servers. Supports both 270 Mb/s and 360 Mb/s data
rates. |
| Set-top
Box: See
STB. |
| SH:
Abbreviation for short-haul. A classification of video
performance under RS-250B/C. Higher performance than long-haul
or medium-haul. |
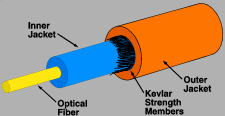
| Sheath:
An outer protective layer of a fiber optic cable.
Also called the cable jacket. |
|
| Shot
Noise:
Noise
caused by current fluctuations arising from the discrete
nature of electrons. |
| Si:
Abbreviation for silicon. Generally used in
detectors. Good for short wavelengths only (e.g., < 1,000
nm). |
| Sideband:
Frequencies distributed above and below the carrier
that contain energy resulting from amplitude
modulation.
The frequencies above the carrier are called upper sidebands,
and the frequencies below the carrier are called lower
sidebands. |
| Silica
Glass:
Glass
made mostly of silicon dioxide, SiO2, used in
conventional optical
fibers. |
| Signal-to-Noise
Ratio (SNR):
The
ratio of the total signal to the total noise which shows how
much higher the signal level is than the level of the noise. A
measure of signal quality. |
| Simple
Network Management Protocol (SNMP):
The Internet
standard protocol for network management software. It monitors
devices on the network, and gathers device performance data
for management information data bases (MIB). |
| Simplex:
Single element (e.g., a simplex connector is a single-fiber
connector). |
| Simplex
Cable:
A term sometimes used for a single-fiber cable. |
| Simplex
Transmission:
Transmission
in one direction only. |

|
| Single
Attachment Concentrator:
A
concentrator
that offers one attachment to the FDDI
network. |
| Single-Line
Laser:
See single-longitudinal
mode laser. |
| Single-Longitudinal
Mode Laser
(SLM):
An injection laser
diode
which has a single dominant longitudinal mode. A single-mode
laser with a side mode suppression ratio (SMSR)< 25 dB. |
|
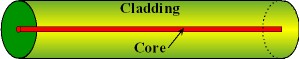
| Single-Mode
(SM) Fiber:
A
small-core
optical
fiber
through which only one mode
will propagate. The typical diameter is 8-9 microns. |
|
| Single-Mode
Laser Diode
(SMLD): See
single-longitudinal
mode laser. |
| Single-Mode
Optical Loss Test Set
(SMOLTS):
An optical
loss test set
for use with single-mode fiber. |
| SI
Units:
Abbreviation
for Système Internationale (in English, International System
of Units), commonly known as the metric system. |
| SLED:
See surface-emitting
diode. |
| SLM:
See single-longitudinal
mode laser. |
| Slope
Efficiency (SE):
This is the mean value of the incremental change in optical
power for an incremental change in forward current when the
device is operating in the lasing region of the optical power
output versus forward current curve. Also referred to as
differential efficiency. |
| SMF:
Abbreviation for single-mode
fiber. |
| SMA:
A threaded type of optical connector.
One of the earliest optical connectors to be widely used.
Offers poor repeatability and performance. |
|
| Smart
Structures:
Also
smart skins. Materials containing sensors (fiber optic or
other types) to measure their properties during fabrication
and use. |
| SMD:
Abbreviation for surface-mount device. See SMT. |
| SMPTE:
Abbreviation for Society of Motion Picture and
Television Engineers. Organization that publishes
ANSI-approved standards, recommended practices, and
engineering guidelines for the motion picture and television
industry. |
http://www.smpte.org |
| SMPTE
259M:
Television standard, written by the Society of Motion Picture
and Television Engineers (SMPTE),
that describes a serial digital interface (SDI) for 10-bit 4:2:2
component and 4fsc
composite digital transport. |
| SMPTE
310M:
Television standard, written by the Society of Motion Picture
and Television Engineers (SMPTE),
that describes a synchronous
serial interface for MPEG-2
digital
transport streams. |
| SMT:
Abbreviation for surface-mount
technology. An electronics manufacturing technique. |
| S/N:
See signal-to-noise
ratio. |
| SNR:
See signal-to-noise
ratio. |
| SOA:
See semiconductor
optical amplifier. |
| Soliton
Pulse:
An optical pulse having a shape, spectral content,
and power level designed to take advantage of nonlinear
effects in an optical fiber waveguide,
for the purpose of essentially negating dispersion
over long distances. |
| SONET:
Abbreviation for synchronous optical network transport system.
An interface standard widely used by the telecom industry
where OC-3 is the lowest current rate (155.5 Mb/s), and OC-768
is the highest rate being contemplated (39.808 Gb/s). Valid
rates increase by a factor of four from the OC-3 rate up to
OC-768. |
|
Source:
In fiber optics, a transmitting LED
or laser
diode,
or an instrument that injects test signals into fibers.
|
| Span
Engineering:
The process of designing a DWDM
transmission span to achieve the required performance based on
fiber type, the transmission distance, amplifier spacing,
noise, power, and channel count. |
| Spectral
Efficiency:
The number of data bits per second that can be transmitted in
a one Hertz bandwidth range. |
| Spectral
Width:
A measure of the extent of a spectrum. For a source,
the width of wavelengths
contained in the output at one half of the wavelength of peak
power. Typical spectral widths are 50 to 160 nm for an LED
and less than 5 nm for a laser
diode. |
|
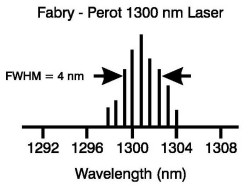
| Spectral
Width, Full Width, Half Maximum
(FWHM): The
absolute difference between the wavelengths
at which the spectral radiant intensity is 50 percent of the
maximum power. |
| Splice:
A permanent connection of two optical
fibers
through fusion or mechanical means. |

|
| Splitter:
see Coupler. |
| Splitting
Ratio:
The ratio of power emerging from two output ports of a coupler. |
| SPM:
See self-phase
modulation. |
| SRS:
See stimulated
Raman scattering. |
| ST:
Abbreviation for straight tip connector.
Popular fiber optic connector originally developed by
AT&T. |

|
| Stabilized
Light Source:
An
LED
or laser
diode
that emits light with a controlled and constant spectral
width,
center
wavelength,
and peak
power
with respect to time and temperature. |
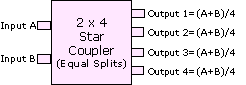
| Star
Coupler:
A coupler
in which power at any input port is distributed to all output
ports. |
|
| Star
Network:
A network
in which all terminals are connected through a single point,
such as a star
coupler
or concentrator. |
| STB:
Abbreviation for set-top box. An auxiliary device that usually
sits on top of or adjacent to a television receiver used in
direct analog or digital satellite transmission and digital
television to view the signals on an analog TV. Converter
boxes are becoming obsolete as old model televisions requiring
a converter are replaced by modern televisions, which
incorporate a converter into the television. Also called a
set-top converter. |
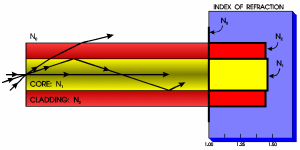
| Step-index
Fiber:
Fiber that has a uniform index
of refraction
throughout the core
that is a step below the index of refraction in the cladding. |
|
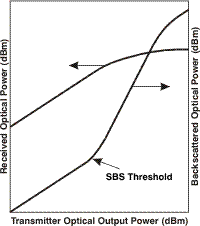
| Stimulated
Brillouin Scattering (SBS):
The easiest fiber nonlinearity
to trigger. When a powerful light wave travels through a fiber
it interacts with acoustical vibration modes in the glass.
This causes a scattering
mechanism to be formed that reflects much of the light back to
the source. |
|
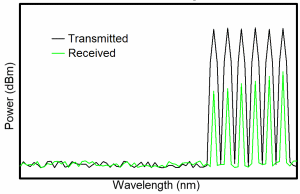
| Stimulated
Raman Scattering (SRS):
A
fiber nonlinearity
similar to SBS but having a much higher threshold. This
mechanism can also cause power to be robbed from shorter
wavelength signals and provide gain to longer wavelength
signals. |
|
| Strength
Member:
The part of a fiber
optic cable
composed of aramid yarn, steel strands, or fiberglass
filaments that increase the tensile strength of the cable. |
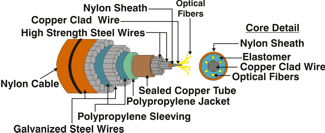
| Submarine
Cable:
A
cable designed to be laid underwater. |
|
| Subscriber
Loop:
Also called local loop.
The link from the telephone company central
office (CO)
to the home or business (customer premises). |
| Sun
Fade:
In satellite systems, the loss of a satellite signal that
occurs when energy from the sun overpowers the satellite's
signal. Also called sun transit or sun outage. |
| Supertrunk:
A cable
that carries several video channels between facilities of a cable
television
company. |
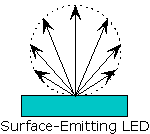
| Surface-emitting
Diode:
A
simple and inexpensive LED
design that emits light from its flat surface rather than its
side with emission spread over a wide angle. |
|
| Surround
Sound:
More commonly referred to as Dolby Digital, a standard for
high-quality digital audio that is used for the sound portion
of video stored in digital
format, especially videos stored on DVD-ROMs. Dolby Digital
delivers 6 channels in the 5:1 format: left, right, and center
screen channels, separate left and right sounds, and a
subwoofer channel. |
| Switch:
1) In communications systems, a mechanical,
electro-mechanical, or electronic device for making, breaking,
or changing the connections in or among circuits. 2) Synonym
for central office, switching center. 3) In communications
systems, to transfer a connection from one circuit to another. |
| Synchronization
Pulse:
1) A signal derived from the composite or combination of the
horizontal and vertical drives. 2) A pulse used to achieve or
maintain synchronism, usually applied to analog signals. (The
term "synchronization bit" is usually applied to
digital data streams.) Commonly called the sync pulse. See
also composite
sync. |
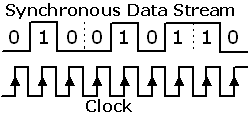
| Synchronous:
A data signal that is sent along with a clock signal.
A system in which events, such as signals, occur at evenly
spaced time durations. Opposite of asynchronous. |
|