| D1: A format for component digital
video tape recording working to the ITU-R 601, 4:2:2 standard using 8-bit sampling. |
| D2: The VTR standard for digital
composite (coded) NTSC or PAL signals that uses data conforming
to SMPTE 244M. |
| D3: A composite digital video
recording format that uses data conforming to SMPTE 244M. |
| D5: An uncompressed tape format for
component digital video which has provisions for HDTV recording by use of 4:1
compression. |
|
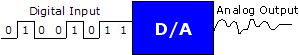
D/A
or
DAC:
Abbreviation for digital-to-analog converter. A
device used to convert digital signals to analog signals.
|
|
|
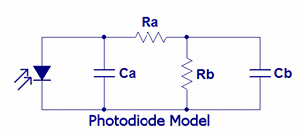
Dark Current:
The induced current that exists in a reversed biased
photodiode
in the absence of incident optical power. It is better understood to be
caused by the shunt resistance of the photodiode. A bias voltage across
the diode (and the shunt resistance) causes current to flow in the
absence of light. (Shunt resistance is Rb in the illustration.)
|
|
| Data
Dependent Jitter:
Also
called data dependent distortion. Jitter
related to the transmitted symbol sequence. DDJ is caused by the limited
bandwidth characteristics, non-ideal individual pulse responses, and
imperfections in the optical channel components. |
|
Data Rate:
The number of bits
of information in a transmission system, expressed in bits per second
(b/s or bps), and which may or may not be equal to the signal or baud
rate.
|
|
dBc:
Abbreviation for
decibel
relative to a carrier level.
|
|
dBµ:
Abbreviation for
decibel
relative to microwatt.
|
|
dBm:
Abbreviation for
decibel
relative to milliwatt.
|
| DBS: Abbreviation for digital
broadcast system. An alternative to
cable and analog satellite reception that uses a
fixed 18-inch dish focused on one or more geostationary satellites. DBS
units receive multiple channels of
multiplexed video and audio signals as well
as programming information, and related data. Also known as digital
satellite system. |
|
DC:
Abbreviation for direct current. An electric current flowing in one
direction only and substantially constant in value.
|
|
DCE:
Abbreviation for data
circuit-terminating equipment. 1) In a data station, the equipment that
performs functions such as signal conversion and coding, at the network
end of the line between the
data terminal equipment (DTE)
and the line, and may be a separate or an integral part of the DTE or of
intermediate equipment. 2) The interfacing equipment that may be
required to couple the data terminal equipment (DTE) into a transmission
circuit or channel and from a transmission circuit of a channel into the
DTE.
|
| DCD:
See Duty Cycle Distortion
Jitter. |
| DCT: See discrete-cosine
transform. |
| DDJ:
See Data Dependent Jitter.
|
|
Decibel
(dB): A unit of measurement indicating
relative power on a logarithmic scale. Often expressed in reference to a
fixed value, such as dBm
or dBµ
.
|
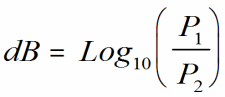
|
| Decoder:
A device used to convert data by reversing the effect of previous coding.
|
|
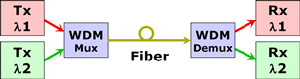
Demultiplexer:
A module that separates two or more signals previously combined by
compatible multiplexing equipment.
|
|
|
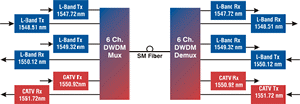
Dense
Wavelength-division Multiplexing (DWDM):
The
transmission of many of closely spaced wavelengths in the 1550 nm region
over a single
optical fiber.
Wavelength spacings are usually 100 GHz or 200 GHz which corresponds to
0.8 nm or 1.6 nm. DWDM bands include the C-Band,
the S-Band,
and the L-Band.
|
(Click to
Enlarge)
|
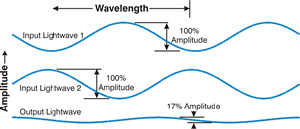
| Destructive
Interference:
Any
interference
that decreases the desired signal. For example, two light waves that are
equal in amplitude and frequency, and out of phase by 180°, will negate
one another. |
|
|
Detector:
An opto-electric transducer used to convert optical power to electrical
current. Usually referred to as a
photodiode.
|
|
DFB:
See
distributed feedback
laser.
|
|
Diameter-mismatch Loss:
The loss of power at a joint that occurs when the transmitting fiber
has a diameter greater than the diameter of the receiving fiber. The
loss occurs when coupling light from a source
to fiber, from fiber to fiber, or from fiber to
detector.
|
|
|
Dichroic Filter:
An
optical filter that transmits light according to wavelength. Dichroic
filters reflect light that they do not transmit. Used in bulk optics
wavelength-division multiplexers.
|
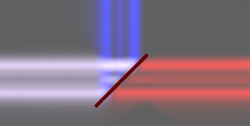 |
|
Dielectric:
Any substance in which an electric field may be
maintained with zero or near-zero power dissipation. This term usually
refers to non-metallic materials.
|
|
Differential Gain
(DG):
A type of
distortion
in a video signal that causes the brightness information to be
incorrectly interpreted.
|
|
Differential Phase
(DP):
A type of
distortion
in a video signal that causes the color information to be incorrectly
interpreted.
|
|
Diffraction Grating:
An array of fine, parallel, equally spaced reflecting or transmitting
lines that mutually enhance the effects of diffraction to concentrate
the diffracted light in a few directions determined by the spacing of
the lines and by the wavelength of the light.
|
 |
|
Digital:
A signal that consists of discrete states. A binary
signal has only two states, 0 and 1. Antonym of analog.
|

|
|
Digital Compression:
A
technique for converting
digital
video to a lower data rate by eliminating redundant information.
|
|
Diode:
An electronic device that lets current flow in only one direction.
Semiconductor diodes used in fiber optics contain a junction between
regions of different doping. They include light emitters (LEDs
and laser diodes)
and detectors
(photodiodes).
|
|
Diode Laser:
Synonymous with injection
laser diode.
|
|
DIP:
Abbreviation for dual in-line package. An electronic package with a
rectangular housing and a row of pins along each of two opposite sides.
|
 |
|
Diplexer:
A device that combines two or more types of
signals into a single output. Often referred to as a
multiplexer
at the transmit end and as a
demultiplexer
at the receiver end.
|

|
|
Directional Coupler:
A
coupling device for separately sampling (through a known coupling loss)
either the forward (incident) or the backward (reflected) wave in a
transmission line.
|
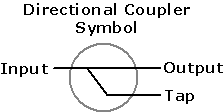
|
|
Directivity:
See
near-end crosstalk.
|
| Discrete-cosine Transform
(DCT): A widely used method of data
compression of digital video pictures that resolves blocks of the
picture (usually 8 x 8 pixels) into frequencies, amplitudes, and colors.
JPEG and DV depend on DCT. |
|
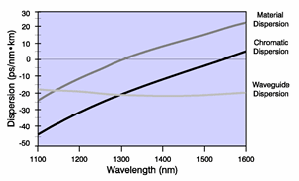
Dispersion:
The temporal spreading of a light signal in an optical waveguide caused
by light signals traveling at different speeds through a fiber either
due to modal or chromatic effects.
|
 |
|
Dispersion-compensating Fiber (DCF):
A fiber
that has the opposite
dispersion
of the fiber being used in a transmission system. It is used to nullify
the dispersion caused by that fiber.
|
|
Dispersion-compensating Module (DCM):
This module has the opposite
dispersion
of the fiber being used in a transmission system. It is used to nullify
the dispersion caused by that fiber. It can be either a spool of a
special fiber or a grating based module.
|
|
Dispersion-shifted Fiber
(DSF):
A type of
single-mode fiber
designed to have zero dispersion near 1550 nm. This fiber type works
very poorly for
DWDM
applications because of high fiber
nonlinearity
at the
zero-dispersion wavelength.
|
|
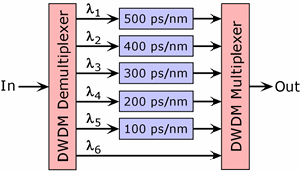
Dispersion
Management:
A technique used in a fiber optic system design to cope with the
dispersion introduced by the optical fiber. A dispersion slope
compensator (illustrated) is one dispersion management technique.
|
|
|
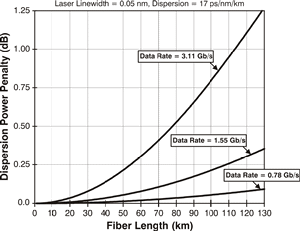
Dispersion Penalty:
The result of
dispersion in which pulses and edges smear making it difficult for the
receiver to distinguish between ones and zeros. This results in a loss
of
receiver sensitivity
compared to a short fiber and measured in dB. The equations for
calculating dispersion penalty are as follows:
|
|
|
Distortion:
nonlinearities
in a unit that cause harmonics and beat products to be generated.
|
|
Distortion-limited Operation:
Generally synonymous with
bandwidth-limited operation.
|
|
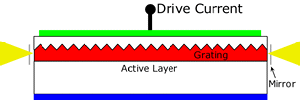
Distributed Feedback Laser
(DFB):
An injection
laser diode
which has a Bragg
reflection grating
in the active region in order to suppress multiple longitudinal modes
and enhance a single longitudinal mode.
|
|
|
Distribution System:
Part
of a cable system consisting of trunk
and feeder
cables used to carry signals from headend
to customer terminals.
|
|
Dominant Mode:
The mode in an optical device spectrum with the most power.
|
|
Dope:
Thick liquid or paste used to prepare a
surface or a varnish-like substance used for waterproofing or
strengthening a material.
|
| Dopant:
An impurity added to an optical medium to change its optical properties. EDFAs
use erbium as a dopant for
optical fiber. |
|
Double-window
Fiber:
1) Multimode
fibers
optimized for 850 nm and 1310 nm operation. 2)
Single-mode fibers
optimized for 1310 nm and 1550 nm operation.
|
|
DSL:
Abbreviation for digital subscriber line. In an integrated
systems digital network (ISDN),
equipment that provides
full-duplex
service on a single twisted metallic pair at a rate sufficient to
support ISDN basic access and additional framing, timing recovery, and
operational functions. See also ISDN.
|
|
DSR:
Abbreviation for data signaling rate. The aggregate rate at which data
pass a point in the transmission path of a data transmission system
expressed in bits per second (bps or b/s).
|
|
DST:
Abbreviation for dispersion supported transmission. In electrical
TDM
systems, a transmission system that would allow data rates at 40 Gb/s by
incorporating devices such as SOAs.
|
|
DSx:
A transmission rate in the North American digital telephone hierarchy.
Also called T-carrier.
|
|
DTE:
Abbreviation for data
terminal equipment. 1) An end instrument that converts user information
into signals for transmission or reconverts the received signals into
user information. 2) The functional unit of a data station that serves
as a data source or a data sink and provides for the data communication
control function to be performed in accordance with link protocol.
|
|
DTR:
Abbreviation for data terminal ready. In a communications network, a
signal from a remote
transmitter
that the transmitter is clear to receive data.
|
| DTV:
Abbreviation for digital television. Any technology, using any of
several digital
encoding schemes, used in connection with the transmission and reception
of television signals. Depending on the transmission medium, DTV often
uses some type of digital
compression
to reduce the required digital data rate. Except for artifacts of the
compression, DTV is more immune (than analog television) to degradation
in transmission, resulting in a higher quality of both audio and video,
to the limits of signal reception. |
|
Dual Attachment Concentrator:
A
concentrator
that offers two attachments to the FDDI
network which are capable of accommodating a dual (counter-rotating)
ring.
|
|
Dual Attachment Station:
A
station that offers two attachments to the FDDI
network which are capable of accommodating a dual (counter-rotating)
ring.
|
|
Dual Ring
(FDDI Dual Ring):
A pair of
counter-rotating
logical rings.
|
|
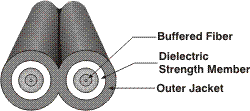
Duplex Cable:
A
two-fiber cable suitable for duplex transmission.
|
 |
|
Duplex Transmission:
Transmission in both directions, either one direction at a time (half-duplex)
or both directions simultaneously (full-duplex).
|
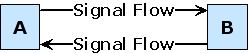
|
|
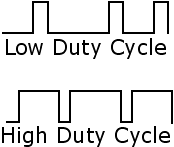
Duty Cycle:
In a digital transmission, the fraction of time a signal is at the high
level.
|
|
|
Duty Cycle Distortion Jitter:
Distortion usually caused by propagation delay differences between
low-to-high and high-to-low transitions. DCD is manifested as a pulse
width distortion of the nominal baud time. |
| DVB-ASI:
Abbreviation for digital video broadcast-asynchronous serial interface.
An interface used to transport MPEG-2
files. The interface consolidates multiple MPEG-2 data streams onto a
single circuit and transmits them at a data rate of 270 Mb/s. |
|
DWDM:
See
dense wavelength-division multiplexing.
|