|
Absorption:
That portion of optical attenuation in optical fiber resulting
from the conversion of optical power to heat. Caused by impurities in
the fiber such as hydroxyl ions. |

|
|
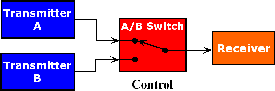
A/B Switch: A device that accepts inputs
(optical or electrical) from a primary path and a secondary path to
provide automatic or manual switching in the event that the primary path
signal is broken or otherwise disrupted. In optical A/B switches,
optical signal power thresholds dictate whether the primary path is
functioning and signals a switch to the secondary path until optical
power is restored to the primary path. |
|
|
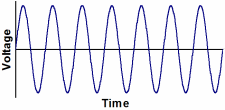
AC:
Abbreviation for alternating current. An electric current that reverses
its direction at regularly recurring intervals. Generally a sinusoidal
waveform. |
 |
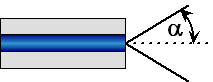
| Acceptance Angle:
The half-angle of the cone (a) within which incident light is totally
internally reflected inside the fiber's
core.
It is equal to sin-1(NA). |
 |
|
Active Device:
A device that requires a source of energy for its operation and has an
output that is a function of present and past input signals. Examples
include power supplies, transistors, LEDs,
Lasers, Detectors,
amplifiers,
and
transmitters.
|
|
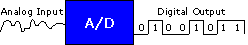
A/D
or
ADC:
Abbreviation for analog-to-digital converter. A device used to convert
analog signals to digital signals. |
 |
|
Add/Drop Multiplexing:
a multiplexing function offered in connection with SONET that allows
lower speed signals to be added or dropped from a high-speed optical
carrier in a wire center. The connection to the add/drop multiplexer is
via a channel to a central office port at a specific digital speed (DS3,
DS1, etc.) |
|
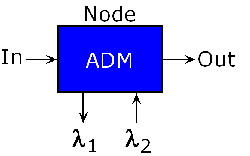
ADM:
Abbreviation for add-drop
multiplexer.
A device which adds or drops signals from a communications network.
Common in CWDM and DWDM systems where a given wavelength is dropped
and/or added at a node.
|
|
|
ADSL:
Abbreviation for
asynchronous
digital subscriber line. See DSL.
|
|
Aerial
Plant:
Cable that is suspended in the air on telephone or electric utility
poles.
|

|
|
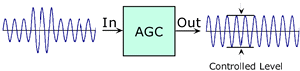
AGC:
Abbreviation for automatic gain control. A process or means by which
gain is automatically adjusted in a specified manner as a function of
input level or another specified parameter. |
|
|
AM:
Abbreviation for amplitude modulation. A transmission technique in which
the amplitude of the carrier varies in accordance with the signal.
|

|
|
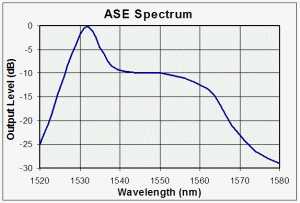
Amplified
Spontaneous Emission (ASE):
A background noise
mechanism common to all types of erbium-doped fiber amplifiers (EDFAs).
It contributes to the noise figure of the EDFA which causes a loss of
signal-to-noise ratio
(SNR).
|
|
|
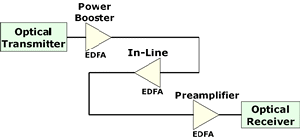
Amplifier:
A device, inserted within a
transmission path, that boosts the strength of an electronic or optical
signal. Amplifiers may be placed just after the
transmitter (power booster), at a distance
between the transmitter and the receiver (in-line amplifier), or just
before the receiver (preamplifier). |
|
|
Analog:
A continuously variable signal. Opposite of
digital. |

|
|
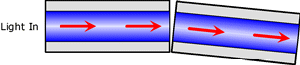
Angular
Misalignment: Loss at a
connector due to fiber end face angles
being misaligned. |
|
|
ANSI:
Abbreviation for American National Standards Institute. An
organization that administers and coordinates the U.S. voluntary
standardization and conformity assessment system.
|
http://www.ansi.org/ |
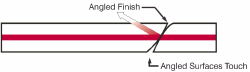
APC:
Abbreviation for angled physical contact. A style of fiber optic
connector with an angle on the connector tip (typically 8°) for the
minimum possible
backreflection. Any backreflection that does
occur exceeds the acceptance angle and that light escapes into the
cladding.
|
|
|
APD: See avalanche photodiode. |
|
APL:
Abbreviation for average picture level. A video quality parameter. |
|
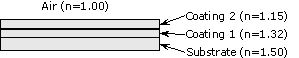
AR Coating: Antireflection coating. A thin,
single or multi-layer dielectric or metallic film applied to an optical
surface to reduce its reflectance and thereby increase its
transmittance. |
|
|
Armor:
A protective layer, usually metal, wrapped around a cable. |
|
ASCII:
Abbreviation for American Standard Code for Information Interchange. An
encoding scheme used to interface between data processing systems, data
communication systems, and associated equipment. |

(Click
to Enlarge)
|
|
ASIC:
Abbreviation for Application-Specific
Integrated Circuit.
A custom-designed integrated circuit. |
|
ASTM:
Abbreviation for American Society for Testing and Materials. An
organization that provides a forum for the development and publication
of voluntary consensus standards for materials, products, systems, and
services that serve as a basis for manufacturing, procurement, and
regulatory activities. |
http://www.astm.org/ |
|
Asynchronous:
Data that is transmitted without an associated clock signal. The time
spacing between data characters or blocks may be of arbitrary duration.
Opposite of
synchronous. |
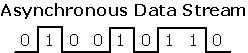
|
| Asynchronous Transfer Mode
(ATM):
A transmission standard widely used by the telecom industry. A digital
transmission switching format with cells containing 5 bytes of header
information followed by 48 data bytes. Part of the B-ISDN standard. |
|
ATE:
Abbreviation for Automatic Test Equipment. Test equipment computer
programmed to perform a number of test measurements on a device without
the need for changing the test setup. Especially useful in testing
components and PCB assemblies. |
|
ATSC: Abbreviation for Advanced
Television Systems Committee. Formed to establish technical standards
for advanced television systems, including digital high definition
television (HDTV). |
http://www.atsc.org |
|
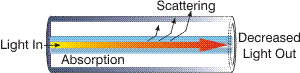
Attenuation:
The decrease in optical level along a fiber optic
waveguide caused by absorption and
scattering. Attenuation is usually expressed in dB/km. |
|
| Attenuation-Limited
Operation:
The condition in a fiber optic link when operation is limited by the
power of the received signal (rather than by bandwidth or distortion). |
|
Attenuator:
1) In electrical systems, a usually passive network for reducing the
amplitude of a signal without appreciably distorting the waveform. 2) In
optical systems, a
passive device for reducing the amplitude of a
signal without appreciably distorting the waveform. |

|
|
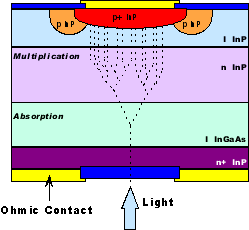
Avalanche
Photodiode (APD): A photodiode that exhibits
internal amplification of photocurrent through avalanche multiplication
of carriers in the junction region. APD's usually require relatively
high bias voltages and are very temperature sensitive. They offer much
better sensitivity than PIN photodiodes. They are limited to digital
applications. |
|
|
Average Power:
The average level of power in a signal that varies with time.
|
|
AWG (Arrayed Waveguide Grating): A device, built with silicon
planar
lightwave circuits (PLC), that allows multiple wavelengths
to be combined and separated in a
dense wavelength-division multiplexing (DWDM) system. |

|
|
Axial
Propagation Constant: For an
optical fiber, the propagation constant evaluated along
the axis of a fiber in the direction of transmission.
The real part of the
axial propagation constant is the attenuation constant. The imaginary
part is the phase constant. |
|
Axis:
The center of an
optical fiber. |
|