| Radiation-hardened
Fiber:
An
optical
fiber
made with core
and cladding
materials that are designed to recover their intrinsic value
of attenuation coefficient, within an acceptable time period,
after exposure to a radiation pulse. |
| Radiometer:
An instrument, distinct from a photometer, to measure
power (Watts) of electromagnetic
radiation. |
| Radiometry:
The science of radiation measurement. |
| Raman
Amplifier: An optical
amplifier
based on Raman scattering
which generates many different wavelengths of light from a
nominally single-wavelength source by means of lasing action
or by the beating together of two frequencies. The optical
signal can be amplified by collecting the Raman scattered
light. |
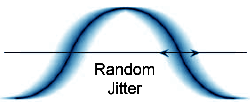
| Random
Jitter (RJ):
Random jitter is due to thermal noise and may be modeled as a Gaussian
process. The peak-to-peak value of RJ is of a probabilistic
nature, and thus any specific value requires an associated
probability. |
|
| Rayleigh
Scattering:
The
scattering
of light that results from small inhomogeneities of material
density or composition. |
| Rays:
Lines that represent the path taken by light. |
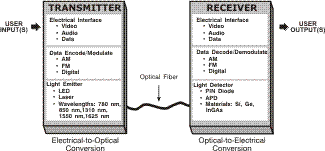
| Receiver:
A terminal device that includes a detector
and signal processing electronics. It functions as an optical-to-electrical
converter. |
|
| Receiver
Overload:
The maximum acceptable value of average received power for an
acceptable BER
or performance. |
| Receiver
Sensitivity:
The
minimum acceptable value of received power needed to achieve
an acceptable BER
or performance. It takes into account power penalties caused
by use of a transmitter
with worst-case values of extinction
ratio,
jitter,
pulse rise times
and fall
times,
optical
return loss,
receiver connector degradations, and measurement tolerances.
The receiver sensitivity does not include power penalties
associated with dispersion,
or backreflections
from the optical path; these effects are specified separately
in the allocation of maximum optical
path penalty.
Sensitivity usually takes into account worst-case operating
and end-of-life (EOL) conditions. |
| Recombination:
Combination of an electron and a hole in a
semiconductor that releases energy, leading to light emission
(in the form of a photon). |
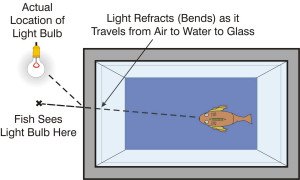
| Refraction:
The changing of direction of a lightwave
in passing through a boundary between two dissimilar media, or
in a graded-index
medium where refractive
index is
a continuous function of position. |
|
| Refractive
Index:
A
property of optical materials that relates to the speed of
light in the material versus the speed of light in a vacuum. |
| Refractive
Index Contrast:
In
an optical
fiber,
a measure of the relative difference in refractive
index
of the core
and cladding.
Symbol is Δ. |
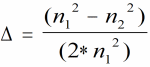
|
| Refractive
Index Gradient:
The description of the value of the refractive
index
as a function of distance from the optical axis
along an optical
fiber
diameter. Also called refractive index profile. |
| Regenerative
Repeater:
A
repeater,
designed for digital transmission, in which digital signals
are amplified, reshaped, retimed, and retransmitted. |

|
| Regenerator:
Synonym for regenerative repeater. |
| Repeater:
A receiver
and transmitter
set designed to regenerate attenuated signals. Used to extend
operating range. |
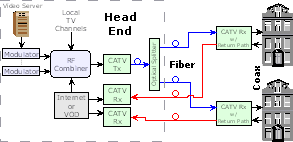
| Return
Path:
A communications connection that carries signals from the
subscriber back to the operator. The return path allows for
interactive television and on-demand services, such as
pay-per-view, video
on demand,
and interactive games. |
(Click
to Enlarge) |
| Residual
Loss:
The loss of the attenuator
at the minimum setting of the attenuator. |
| Responsivity:
The ratio of a photodetectors
electrical output to its optical input in Amperes/Watt (A/W). |
| Return
Loss: See optical
return loss. |
| RF:
Abbreviation for radio frequency. Any frequency within the electromagnetic
spectrum
normally associated with radio wave propagation. |
| RF
Carrier:
An AM
technique wherein a carrier, with a frequency much higher than
the encoded information, varies according to the amplitude of
the information being encoded. |
| RFI:
Abbreviation for radio frequency interference. Synonym for electromagnetic
interference. |
| RGB:
Abbreviation for red, green, and blue. The basic
parallel component set in which a signal is used for each
primary color, or the related equipment or interconnect
formats or standards. |
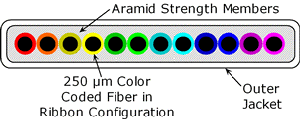
| Ribbon
Cables:
Cables
in which many fibers
and/or copper wires are embedded in a plastic material in
parallel, forming a flat ribbon-like structure. |
 |
| RIN:
Abbreviation for relative intensity noise. Often used
to quantify the noise characteristics of a laser. |
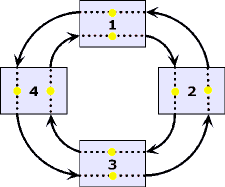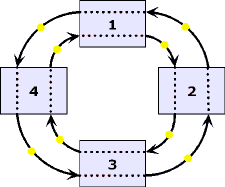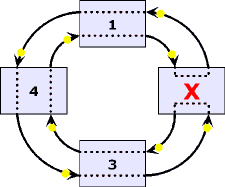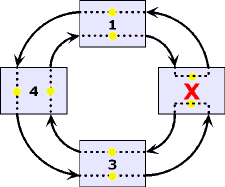
| Ring:
A set of stations wherein information is passed sequentially
between stations, each station in turn examining or copying
the information, and finally returning it to the originating
station. |
| Ring
Network:
A network
topology
in which terminals are connected in a point-to-point serial
fashion in an unbroken circular configuration. |
|
| Rise
Time:
The
time taken to make a transition from one state to another,
usually measured between the 10% and 90% completion points of
the transition. Alternatively the rise time may be specified
at the 20% and 80% amplitudes. Shorter or faster rise times
require more bandwidth
in a transmission channel. |
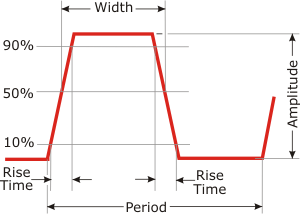 |
| RJ:
See Random
Jitter. |
| RMS:
Abbreviation for root mean square. Technique used to measure
AC voltages. |
| RS-250C:
An ANSI
recommended standard for video transmission used to evaluate
the quality of a received picture quality. Different
requirements exist for short-haul,
medium-haul,
and long-haul
RS-250C. Each of these three levels is defined by the number
of intermediate processing devices and the type of path
(optical or electrical). |
| RTS:
Abbreviation for request to send. In a communications network,
a signal from a remote receiver
to a transmitter
for data to be sent to that receiver. |
| RZ:
Abbreviation for return to zero. A common means of encoding
data that has two information states called zero and
one in which the signal returns to a rest state during a
portion of the bit period. |