|
IC: See integrated
circuit. |
|
ICEA:
Abbreviation for Insulated Cable Engineers Association. A technical
professional organization that contributes to the standards of insulated
cable in these four areas: power cables, communication cables, portable
cables, and control and instrumentation. Within this organization there
are subcommittees that concentrate on one of the four areas. |
http://www.icea.net/ |
|
IDP: See
integrated
detector/preamplifier.
|
| IEEE:
Abbreviation for Institute of Electrical and
Electronic Engineers. A technical professional association that
contributes to voluntary standards in technical areas ranging from
computer engineering, biomedical technology and telecommunications, to
electric power, aerospace and consumer electronics, among others. |
http://www.ieee.org/ |
| IF:
Abbreviation for Intermediate Frequency. A frequency to which a carrier
frequency is shifted as an intermediate step in transmission or
reception. |
|
IIN: See
interferometric intensity noise.
|
|
Impedance: The total passive opposition offered to the flow of
electric current. Determined by the particular combination of
resistance, inductive reactance, and capacitive reactance in a given
circuit. A function of frequency, except when in a purely resistive
network. |
|
Impedance Matching: The connection of an additional impedance to an existing
one in order to achieve a specific effect, such as to balance a circuit
or to reduce reflection in a transmission line. |
|
Index-matching Fluid:
A fluid whose
index of refraction
nearly equals that of the fibers
core. Used to reduce
Fresnel reflection
loss at fiber ends. Also known as index-matching gel. |
|
Index of Refraction:
The ratio of the velocity of light in free space to the velocity of
light in a fiber material. Always greater than or equal to one. Also
called refractive index. |
|
|
Infrared (IR): The
region of the
electromagnetic spectrum
bounded by the long-wavelength extreme of the visible spectrum (about
0.7 µm, or 700 nm) and the shortest microwaves (about 0.1 µm or 100 nm). |
| Infrared Emitting
Diodes:
LEDs that emit infrared energy
(830 nm or longer). |
|
Infrared Fiber:
Colloquially, optical fibers with best transmission at wavelengths of
2,000 nm (2 µm) or longer, made of materials other than silica glass.
See also
fluoride glasses. |
|
InGaAs:
Abbreviation for indium gallium arsenide. Generally used to make
high-performance long-wavelength
detectors.
|
|
InGaAsP:
Abbreviation for indium gallium
arsenide phosphide. Generally used for long-wavelength light emitters. |
| Injection
Laser Diode (ILD):
A
laser employing a forward-biased
semiconductor junction as the active medium. Stimulated emission of
coherent light occurs at a PIN junction where electrons and holes are
driven into the junction. |
|
In-line Amplifier:
An
EDFA or other type of
amplifier
placed in a transmission line to strengthen the attenuated signal for
transmission onto the next, distant site. In-line amplifiers are
all-optical devices. |

|
|
InP: Indium
Phosphide. A semiconductor material used to make
optical amplifiers
and
HBTs.
|
|
Insertion Loss:
The loss of power that results from inserting a component, such as a
connector,
coupler
(illustrated), or
splice,
into a previously continuous path. |
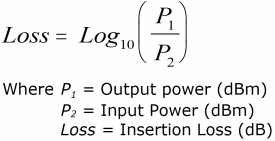
|
| Integrated
Circuit (IC):
An electronic circuit that consists of many individual circuit elements,
such as transistors, diodes, resistors, capacitors, inductors, and other
passive
and
active
semiconductor devices, formed on a single chip of semiconducting
material and mounted on a single piece of substrate material. |
| Integrated
Detector/Preamplifier
(IDP): A detector package
containing a PIN
photodiode
and transimpedance amplifier. |
| Integrated
Systems Digital Network
(ISDN): An integrated
digital network in which the same time-division switches and digital
transmission paths are used to establish connections for services such
as telephone, data, electronic mail and facsimile. How a connection is
accomplished is often specified as a switched connection, non-switched
connection, exchange connection, ISDN connection, etc. |
|
Intensity: The square
of the electric field strength of an electromagnetic wave. Intensity is
proportional to
irradiance and is sometimes used
in place of the term "irradiance" when only relative values are
important. |
|
Intensity Modulation (IM):
In optical communications, a form of modulation in which the optical
power output of a source varies in accordance with some characteristic
of the modulating signal. |
|
Interchannel Isolation:
The ability to prevent
undesired optical energy from appearing in one signal path as a result
of coupling from another signal path. Also called
crosstalk.
|
|
Interference: Any extraneous energy, from natural or manmade sources,
that impedes the reception of desired signals. The interference may be
constructive or
destructive, resulting in increased or decreased amplitude,
respectively.
|
|
Interferometer:
An instrument that uses the principle of interference of electromagnetic
waves for purposes of measurement. Used to measure a variety of physical
variables, such as displacement (distance), temperature, pressure, and
strain. |
|
Interferometric Intensity Noise (IIN):
Noise generated in optical fiber caused by the distributed
backreflection
that all fiber generates mainly due to
Rayleigh scattering.
OTDRs make use of this scattering
power to deduce the fiber loss over distance. |
| Interferometric
Sensors:
Fiber optic sensors that rely on
interferometric detection. |
| Inter-LATA:
1. Between local access and transport areas (LATAs). 2. Services,
revenues, and functions related to telecommunications that begin in one
LATA and that terminate in another or that terminate outside of the
LATA. |
|
Intermodulation (Mixing):
A fiber
nonlinearity
mechanism caused by the power dependant refractive index of glass.
Causes signals to beat together and generate interfering components at
different frequencies. Very similar to
four wave mixing. |
| International
Telecommunications Union (ITU):
A civil international organization, headquartered in Geneva,
Switzerland, established to promote standardized telecommunications on a
worldwide basis. The ITU-R and the ITU-T are committees under the ITU,
which is recognized by the United Nations as the specialized agency for
telecommunications. |
http://www.itu.int/home/index.html |
|
Internet:
A worldwide collection of millions of computers
that consists mainly of the world wide web and e-mail. |
|
Intersymbol Interference:
1) In a digital transmission system,
distortion
of the received signal, manifested in the temporal spreading and
consequent overlap of individual pulses to the degree that the
receiver
cannot reliably distinguish between changes of state, i.e., between
individual signal elements. At a certain threshold, intersymbol
interference will compromise the integrity of the received data.
Intersymbol interference may be measured by
eye patterns. |
|
Intrinsic Losses:
Splice losses arising from differences in
the fibers being spliced. |
| IP:
Abbreviation for Internet protocol. A standard
protocol, developed by the DOD, for use in interconnected systems of
packet-switched computer communications networks. |
| IPI:
Abbreviation for intelligent peripheral interface
as defined by ANSI X3T9.3 document. |
|
IR: See
infrared.
|
|
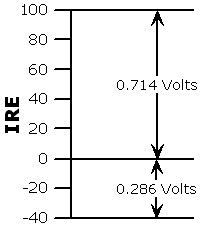
IRE Unit:
An arbitrary unit created by the Institute of Radio Engineers to
describe the amplitude characteristic of a video signal, where pure
white is defined as 100 IRE with a corresponding voltage of 0.714 Volts
and the blanking level is 0 IRE with a corresponding voltage of 0.286
Volts.
|
|
|
Irradiance: Power per
unit area. |
| ISA:
Abbreviation for Instrumentation,
Systems, and Automation Society. An international, non-profit, technical
organization. The society fosters advancement of the use of sensors,
instruments, computers, and systems for measurement and control in
variety of applications |
http://www.isa.org/ |
|
ISDN: See
integrated
services digital network.
|
| ISO:
Abbreviation for International Standards Organization. Established in
1947, ISO is a worldwide federation of national standards committees
from 140 countries. The organization promotes the development of
standardization throughout the world with a focus on facilitating the
international exchange of goods and services, and developing the
cooperation of intellectual, scientific, technological, and economical
activities. |
http://www.iso.ch/iso/en/ISOOnline.frontpage |
| ISP: Abbreviation for
Internet service provider. A company or organization that provides
Internet connections to individuals or companies via dial-up, ISDN, T1,
or some other connection. |
|
Isolation:
See
near-end crosstalk.
|
|
ITU: See
International Telecommunications Union.
|