|
Half-duplex
Transmission:
A
bidirectional
link that is limited to one-way transfer of data, i.e., data cannot be
sent both ways at the same time. Also referred to as
simplex transmission.
An example is the operation of a push-to-talk walkie talkie. |

|
|
Hard-clad Silica Fiber:
An
optical fiber
having a silica core
and a hard plastic cladding.
|
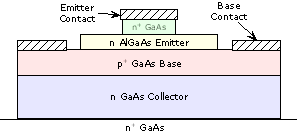
| HBT:
Abbreviation for heterojunction bipolar
transistors. A very high performance transistor structure built using
more than one semiconductor material. Used in high performance wireless
telecommunications circuits such as those used in digital cell phone
handsets and high-bandwidth fiber optic systems. |
|
| HDSL:
Abbreviation for high data-rate digital subscriber line. A DSL
operating at a high data rate compared to the data rates specified for
ISDN.
|
| HDTV:
Abbreviation for high-definition television. Television that has
approximately twice the horizontal and twice the vertical emitted
resolution specified by the NTSC standard. |
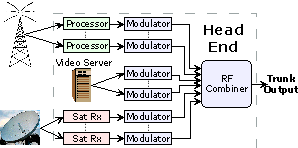
| Headend:
1) A
central control device required within some LAN
and MAN
systems to provide such centralized functions as remodulation, retiming,
message accountability, contention control, diagnostic control, and
access to a gateway. 2) A central control device within
CATV
systems to provide such centralized functions as remodulation
(illustrated). See also local area
network (LAN). |
|
| Hero
Experiments:
Experiments performed in a laboratory environment to test the limits of
a given technology. |
| Hertz
(Hz):
One cycle per second. |
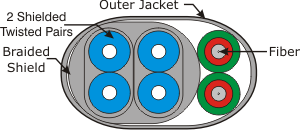
| HFC (Hybrid Fiber Coax):
A transmission system or cable construction (illustrated) that
incorporates both fiber optic transmission components and copper coax
transmission components. |
|
| HFC Network:
A telecommunication technology in which
optical fiber
and
coaxial cable
are used in different sections of the network to carry broadband
content. The network allows a CATV
company to install fiber from the cable
headend
to serve nodes
located close to business and homes, and then from these fiber nodes,
use coaxial cable to individual businesses and homes. |
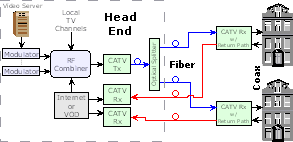
(Click to Enlarge)
|
| HIPPI:
Abbreviation for high performance parallel
interface as defined by the ANSI X3T9.3 document, a standard technology
for physically connecting devices at short distances and high speeds.
Primarily to connect supercomputers and to provide high-speed backbones
for local area
networks
(LANs). |
| Hot Swap:
In an electronic device subassembly or component, the act or process of
removing and replacing the subassembly or component without first
powering down the device. |
|
HP:
Abbreviation for homes passed. Homes that could easily and inexpensively
be connected to a cable network because the feeder cable is nearby. |
| Hydrogen
Losses:
Increases in fiber connector
attenuation
that occur when hydrogen diffuses into the glass matrix and absorbs some
light. |