|
G:
Abbreviation for giga. One billion or 109.
|
| GaAlAs:
Abbreviation for gallium aluminum arsenide. Generally used for short
wavelength light emitters. |
| GaAs:
Abbreviation for gallium arsenide. Used in light emitters. |
| Gain:
The ratio of output current, voltage, or power to input current,
voltage, or power, respectively. Gain is usually expressed in dB.
If the ratio is less than unity, the gain, expressed in dB, will be
negative, in which case there is a loss
between input and output. |
| GaInAsP:
Abbreviation for gallium indium arsenide
phosphide. Generally used for long wavelength light emitters. |
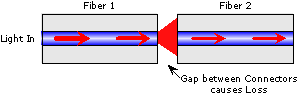
| Gap Loss:
Loss resulting from the end separation of two axially aligned
fibers.
|
|
| Gate:
1) A device having one output channel and one or
more input channels, such that the output channel state is completely
determined by the input channel states, except during switching
transients. 2) One of the many types of combinational logic elements
having at least two inputs. |
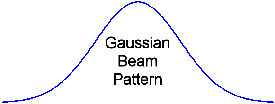
Gaussian Beam:
A
beam pattern used to approximate the distribution of energy in a fiber
core. It can also be used to describe emission patterns from
surface-emitting LEDs.
Most people would recognize it as the bell curve (illustrated). The
Gaussian beam is defined by the equation:
E(x) = E(0)e-x2/w02
|
|
| GBaud:
One billion bits of data per second or 109 bits. Equivalent
to 1 for binary signals. |
| Ge:
Abbreviation for germanium. Generally used in
detectors.
Good for most fiber optic wavelengths (e.g., 800-1600 nm). Performance
is inferior to InGaAs due to smaller energy gap which causes higher
noise and temperature sensitivity. |
| Genlock:
A process of sync generator locking. This is
usually performed by introducing a composite video signal from a master
source to the subject sync generator. The generator to be locked has
circuits to isolate vertical drive, horizontal drive and subcarrier. The
process then involves locking the subject generator to the master
subcarrier, horizontal, and vertical drives so that the result is that
both sync generators are running at the same frequency and phase. |
| GHz:
Abbreviation for gigahertz. One billion Hertz
(cycles per second) or 109
Hertz. |
|
Graded-index Fiber:
Optical fiber
in which the
refractive index
of the core is in the form of a parabolic curve, decreasing toward the
cladding.
|

|
| GRIN:
Abbreviation for gradient index. Generally refers to the SELFOC lens
often used in fiber optics. |
| Ground Loop
Noise:
Noise that results when equipment is grounded at points having different
potentials thereby creating an unintended current path. The
dielectric
properties of
optical fiber
provide electrical isolation that eliminates ground loops.
|
| Group Index:
Also called
group refractive index. In fiber optics, for a given mode propagating in
a medium of refractive index (n), the group index (N), is the velocity
of light in a vacuum (c), divided by the group velocity of the mode.
|
| Group Velocity:
1)
The velocity of propagation of an envelope produced when an
electromagnetic wave is modulated by, or mixed with, other waves of
different frequencies. 2) For a particular mode, the reciprocal of the
rate of change of the phase constant with respect to angular frequency.
3) The velocity of the modulated optical power.
|