|
OADM: See optical
add/drop multiplexer.
|
| OAM:
Abbreviation for operation, administration, and maintenance.
Refers to telecommunications networks. |
|
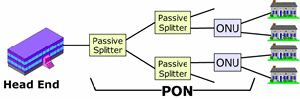
OAN:
Abbreviation for optical access network. A network technology,
based on passive
optical networks (PONs),
that includes an optical switch at the central
office, an intelligent
optical terminal at the customers premises, and a passive
optical network between the two, allowing services providers
to deliver fiber-to-the-home
while eliminating the expensive electronics located outside
the central office.
|
 |
| OCH:
See optical
channel. |
| OC-x:
Abbreviation for optical carrier. A carrier rate
specified in the SONET
standard. |
| ODN:
Abbreviation for optical distribution network. Term for
optical networks being developed for interactive video, audio,
and data distribution. |
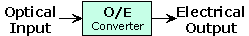
| O/E:
Abbreviation for
optical-to-electrical converter. A device used to convert
optical signals to electrical signals. Also known as OEC. |
|
| OEIC:
Abbreviation for opto-electronic integrated circuit.
An integrated
circuit that includes
both optical and electrical elements. |
| OEM:
Abbreviation for original equipment manufacturer. The
manufacturer of any device that is designed and built to be
distributed under the label of another company. |
| OLT:
Abbreviation for optical line termination. Optical network
elements that terminate a line signal. |
| OLTS:
Abbreviation for optical loss test set. A source
and optical
power meter combined
used to measure optical loss. |
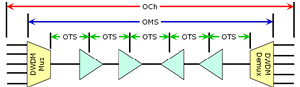
| OMS:
Abbreviation for
optical multiplex section. A section of a DWDM
system that incorporates an optical
add/drop multiplexer. |
|
| ONI:
Abbreviation for optical network interface. A device used in
an optical distribution network to connect two parts of that
network. |
 |
|
ONT:
Abbreviation for optical network termination. Optical network
element that terminates a line signal in installations where
the fiber extends into the customer premises.
|
| ONU:
Abbreviation for optical network unit. A network element that
is part of a fiber-in-the-loop
system. |
| OOI:
Abbreviation for open optical interface. A point at which an
optical signal is passed from one equipment medium to another
without conversion to an electrical signal. |
| Open
Systems Interconnection
(OSI): Pertaining
to the logical structure for communications networks
standardized by the International
Organization for Standardization (ISO). |
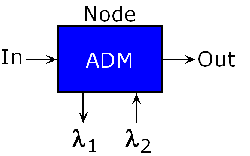
| Optical
Add/Drop Multiplexer (OADM):
A device which adds or drops individual wavelengths from a DWDM
system. |
|
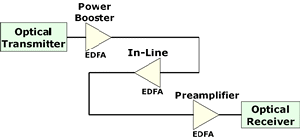
| Optical
Amplifier:
A device that amplifies an input optical signal without
converting it into electrical form. The best developed are
optical fibers doped with the rare earth element, erbium. See
also EDFA. |
|
| Optical
Bandpass:
The range of optical wavelengths which can be transmitted
through a component. |
| Optical
Channel:
An optical wavelength band for WDM
optical communications. |
| Optical
Channel Spacing:
The wavelength separation between adjacent WDM
channels. |

|
| Optical
Channel Width: The
optical wavelength range of a channel. |
| Optical
Continuous Wave Reflectometer
(OCWR): An
instrument used to characterize a fiber
optic link wherein an
unmodulated signal is transmitted through the link, and the
resulting light scattered
and reflected back to the input is measured. Useful in
estimating component reflectance and link optical return loss. |
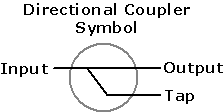
| Optical
Directional Coupler
(ODC): A component
used to combine and separate optical power. |
|
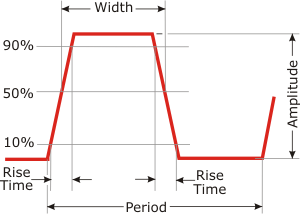
| Optical
Fall Time: The
time interval for the falling edge of an optical pulse
to transition from 90% to 10% of the pulse amplitude.
Alternatively, values of 80% and 20% may be used. |
|
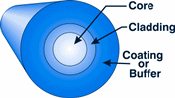
| Optical
Fiber: A
glass or plastic fiber that has the ability to guide light
along its axis.
The three parts of an optical fiber are the core,
the cladding,
and the coating
or buffer. |
|
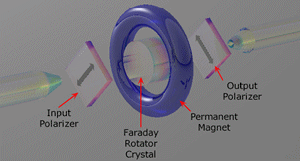
| Optical
Isolator: A
component used to block out reflected and unwanted light. Also
called an isolator. |
|
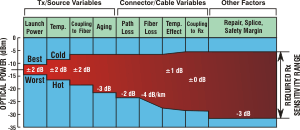
| Optical
Link Loss Budget:
The range of
optical loss over which a fiber
optic link will operate
and meet all specifications. The loss is relative to the transmitter
output power and affects the required receiver
input power. |
(Click
to Enlarge.)
|
| Optical
Path Power Penalty:
The additional
loss budget required to account for degradations due to
reflections, and the combined effects of dispersion
resulting from intersymbol
interference,
mode-partition noise, and laser chirp. |
 |
| Optical
Power Meter:
An instrument that measures the amount of optical power
present at the end of an optical fiber
or cable. |

|
| Optical
Pump Laser:
A shorter wavelength laser
used to pump a length of fiber with energy to provide
amplification at one or more longer wavelengths. See also EDFA. |
| Optical
Return Loss (ORL):
The ratio
(expressed in dB)
of optical power reflected by a component or an assembly to
the optical power incident on a component port when that
component or assembly is introduced into a link or system. |
| Optical
Rise Time: The
time interval for the rising edge of an optical pulse
to transition from 10% to 90% of the pulse amplitude.
Alternatively, values of 20% and 80% may be used. |

|
| Optical
Signal-to-Noise-Ratio (OSNR):
The optical equivalent of SNR. |
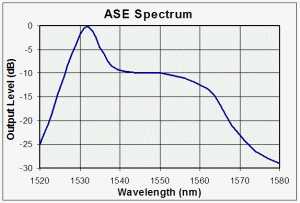
| Optical
Spectrum Analyzer (OSA):
A device that
allows the details of a region of an optical spectrum to be
resolved. Commonly used to diagnose DWDM
systems. |
 |
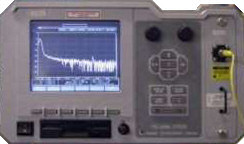
| OTDR
(Optical Time Domain Reflectometer):
An instrument that locates faults in optical
fibers or infers attenuation
by backscattered
light measurements. |
 |
| Optical
Waveguide: Another
name for optical
fiber. |
| OSA:
See optical
spectrum analyzer. |
| OSNR:
See optical
signal-to-noise ratio. |
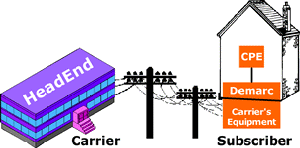
| Outside
Plant (OSP):
In telephony, all cables, conduits, ducts, poles, towers,
repeaters, repeater huts, and other equipment located between
a demarcation point in a switching facility and a demarcation
point in another switching facility or customer premises. |
|
| OXC:
Abbreviation for optical cross-connect. See cross-connect. |