| p:
Abbreviation for pico. One trillionth or 10-12.
|
| pA:
Abbreviation for picoamp. One trillionth of an Amp
or 10-12 Amps. |
| PABX:
Abbreviation for private automatic branch
exchange. See PBX.
|
|
Packet:
In data communications, a sequence of binary
digits, including data and control signals, that is transmitted and
switched as a composite whole. The packet contains data, control
signals, and possibly error control information, arranged in a specific
format.
|
|
Packet Switching:
The process of routing and transferring data by means of addressed
packets
so that a channel is occupied during the transmission of the packet
only, and upon completion of the transmission the channel is made
available for the transfer of other traffic.
|
| PAL:
Abbreviation for phase alternation by line. A composite color standard
used in many parts of the world for TV broadcast. The phase alternation
makes the signal relatively immune to certain distortions (compared to
NTSC).
Delivers 625 lines at 50 frames per second. PAL-plus is an
enhanced-definition version. |
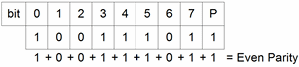
| Parity:
A term used in binary
communication systems to indicate whether a number of 1’s in a
transmission plus a parity bit is even or odd. If the total number of
1’s is even, the parity is said to be even; if the total number of 1’s
is odd, the parity is said to be odd. |
|
| Passband:
The region of usable frequency in electronics or wavelength in optics.
|
|
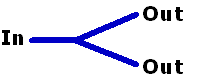
Passive Branching Device:
A device which divides an optical input into two or more optical
outputs. |
|
| Passive Device:
Any device that does not require a source of energy for its operation.
Examples include electrical resistors or capacitors, diodes,
optical fiber
(photo), cable,
wires, glass, lenses, and filters.
|

|
|
Pathological Test Code:
A special test pattern used with DTV
and HDTV
signals to create the longest strings of zeros and ones over the serial
link. This requires the serial transport link to handle much lower
frequency components than is typical in a normal data link.
|
| Pay-Per-View (PPV):
An event that has an associated viewing cost, and which may be purchased
separately from any package or subscription. The ordered events could
include movies, special events, such as sporting, or adult programming.
The event could be purchased by either impulse PPV by using a television
remote (this application requires a continuous land line phone based
connection), or over the phone PPV (this application may have additional
costs for processing). |
| PBX:
Abbreviation for private branch exchange. A subscriber-owned
telecommunications exchange that usually includes access to public
switched networks. |
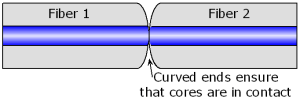
| PC:
Abbreviation for physical contact. Refers to an optical
connector
that allows the fiber
ends to physically touch. Used to minimize
backreflection
and
insertion loss. |
|
| PCB:
Abbreviation for printed circuit board. Also referred to as PWB (printed
writing board). |
|
PCM:
See pulse-code modulation.
|
|
PCS
Fiber:
See plastic clad silica.
|
|
PD:
See photodiode.
|
| Peak Power
Output:
The
output power averaged over that cycle of an electromagnetic wave having
the maximum peak value that can occur under any combination of signals
transmitted. |
| Peak
Wavelength:
In optical emitters, the spectral line having the greatest output power.
Also called peak emission wavelength. |
| PFM:
Abbreviation for pulse-frequency modulation. Also referred to as square
wave FM.
|
| Phase Constant:
The
imaginary part of the axial propagation constant for a particular mode,
usually expressed in radians per unit length. See also
attenuation.
|
| Phase Noise:
Rapid,
short-term, random fluctuations in the phase of a wave caused by
time-domain instabilities in an oscillator. |
|
Phase-Shift Keying (PSK):
1) In digital transmission, angle modulation in which the phase of the
carrier discretely varies in relation, either to a reference phase or to
the phase of the immediately preceding signal element, in accordance
with data being transmitted. 2) In a communications system, the
representation of characters, such as bits
or quaternary digits,
by a shift in the phase of an electromagnetic carrier wave with respect
to a reference, by an amount corresponding to the symbol being encoded.
Also called biphase modulation, phase-shift signaling. |
|
Photoconductive:
Losing an electrical charge on exposure to light.
|
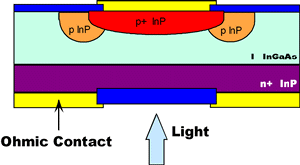
| Photodetector:
An optoelectronic transducer such as a PIN photodiode
(illustrated) or
avalanche photodiode.
In the case of the PIN diode, it is so named because it is constructed
from materials layered by their positive, intrinsic, and negative
electron regions. |
|
| Photodiode
(PD):
A semiconductor device that converts light to electrical current.
|
| Photon:
A quantum of electromagnetic energy. A particle of light.
|
| Photonic:
A term coined for devices that work using photons, analogous to the
electronic for devices working with electrons. |
|
Photovoltaic:
Providing an electric current under the influence of light or similar
radiation. |
| Pigtail:
A short
optical fiber
permanently attached to a source,
detector,
or other fiber optic device at one end and an optical
connector
at the other. |
|
| PIN Photodiode:
See photodiode. |
| Planar
Waveguide:
A
waveguide
fabricated in a flat material such as thin film. |
| Plastic
Clad Silica
(PCS):
Also called hard clad
silica (HCS). A
step-index fiber
with a glass core
and plastic or polymer cladding
instead of glass. |
| Plastic Fiber:
An
optical fiber
having a plastic core
and plastic cladding.
|
| PLC:
Abbreviation for
planar lightwave circuit. A device which incorporates a planar
waveguide. |
| Plenum:
The air handling space between walls, under structural floors, and above
drop ceilings, which can be used to route intrabuilding cabling. |
| Plenum Cable:
A cable
whose flammability and smoke characteristics allow it to be routed in a
plenum area without being enclosed in a conduit. |
| PMD:
See
polarization mode dispersion. |
|
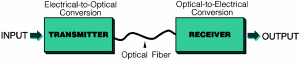
Point-to-Point Transmission:
Transmission between two designated stations. |
|
|
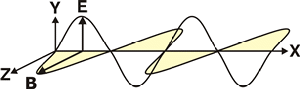
Polarization:
The direction of the electric field in the
lightwave.
If the electric field of the lightwave is in the Y Axis, the light
is said to be vertically polarized. If the electric field of the
lightwave is in the X axis, the light is said to be horizontally
polarized. |
|
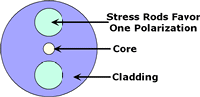
| Polarization Maintaining
Fiber:
Fiber designed to propagate only one
polarization of light that enters it.
|
|
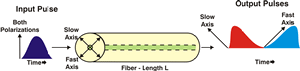
| Polarization Mode Dispersion (PMD): Polarization mode dispersion is
an inherent property of all optical media. It is caused by the
difference in the propagation velocities of light in the orthogonal
principal polarization states of the transmission medium. The net effect
is that if an optical
pulse contains both
polarization components, then the different
polarization components will travel at different speeds and arrive at
different times, smearing the received optical signal.
|
(Click
to Enlarge)
|
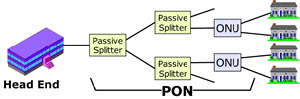
| PON: Abbreviation for passive optical
network. A broadband fiber optic access network that uses a means of
sharing fiber to the home without running individual fiber optic lines
from an exchange point, telco
Central Office (CO),
or a CATV
headend
and the subscriber’s home. |
 |
| Port:
Hardware entity at each end of the link. |
| POTS:
Abbreviation for plain old telephone system. A call that requires
nothing more than basic call handling without additional features. |
| p-p:
Abbreviation for peak-to-peak. The algebraic difference between extreme
values of a varying quantity. |
| PPM:
Abbreviation for pulse-position modulation. A method of encoding
data. |
|
Preform:
The glass rod from which
optical fiber
is drawn. |
|
Profile Dispersion:
Dispersion in an optical fiber attributed to
the variation of
refractive index contrast with
wavelength.
|
| ps:
Abbreviation for picosecond. One trillionth of a second or 10-12
seconds. |
| PSTN: Abbreviation for public switched
telephone network. A domestic telecommunications network usually
accessed by telephones, key telephone systems, private branch
exchange trunks, and data arrangements. |
|
Public Switched Networks (PSN): 1. Any common carrier network
that provides circuit switching among public users. 2. A switched
network accessible to the public for originating and terminating
telecommunications messages. 3. Any common carrier switched network,
whether by wire or radio, including local exchange carriers,
interexchange carriers, and mobile service providers, that use the North
American Numbering Plan in common with provision of switched services. |
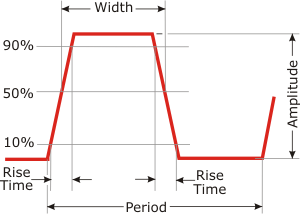
| Pulse:
A current or voltage which changes abruptly from one value to
another and back to the original value in a finite length of time. Used
to describe one particular variation in a series of wave motions. The
parts of the pulse include the rise
time, fall
time, and pulse width, pulse
amplitude. The period of a pulse refers to the amount of time between
pulses. |
 |
| Pulse-code Modulation (PCM):
A technique in which an analog
signal, such as a voice, is converted into a digital signal by sampling
the signal's amplitude and expressing the different amplitudes as a binary number. The
sampling rate must be at least twice the
highest frequency in the signal. |
|
Pulse Dispersion: The
dispersion of an optical signal as it
propagates through an
optical fiber. Also called pulse spreading. |
| Pump Laser: A power source for signal
amplification, typically a 980 nm or 1480 nm laser, used in
EDFA applications. |
| Push: 1) In electronic marketing, to
send data to another computer without a direct request from that
computer. 2) In networking, to send data from a server to a client in
compliance with a previous request from the client, as soon as the data
becomes available. |
|
pW:
Abbreviation for picowatt. One trillionth of a Watt or 10-12
Watts.
|