|
F:
Abbreviation for Fahrenheit. Measure of temperature where pure water
freezes at 32° and boils at 212°.
|
|
Fabry
Perot:
See FP. |
|
Failure Rate:
See
FIT Rate.
|
|
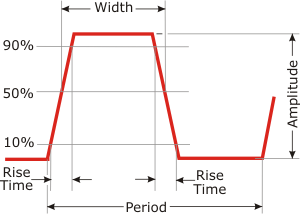
Fall Time:
Also called turn-off time. The time required for the trailing edge of a
pulse to fall from 90% to 10% of its amplitude; the time required for a
component to produce such a result. Typically measured between the 90%
and 10% points or alternately the 80% and 20% points.
|
|
|
FAR:
Abbreviation for federal acquisition regulation. The guidelines by which
the U.S. government purchases goods and services. Also the criteria that
must be met by the vendor in order to be considered as a source for
goods and services purchased by the U.S. government.
|
|
Faraday Effect:
A
phenomenon that causes some materials to rotate the
polarization
of light in the presence of a magnetic field parallel to the direction
of propagation. Also called magneto-optic effect.
|
|
Far-End Crosstalk:
See
wavelength isolation.
|
|
FBG:
Abbreviation for fiber Bragg gratings. See Bragg
grating.
|
| FC/APC:
A threaded optical connector that uses a
special curved polish and angled tip on the connector for very low
backreflection.
Used with single-mode or fiber only. |

|
|
FCC:
Abbreviation for Federal Communications Commission. The U.S. Government
board of five presidential appointees that has the authority to regulate
all non-Federal Government interstate telecommunications as well as all
international communications that originate or terminate in the United
States.
|
|
|
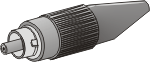
FC/PC:
A threaded optical connector that uses a special
curved polish on the connector for low
backreflection.
Good for single-mode or multimode fiber.
|
|
|
FCS:
Abbreviation for frame check sequence. An error-detection scheme that
(a) uses parity bits generated by polynomial encoding of digital
signals, (b) appends those parity bits to a digital signal, and (c) uses
decoding algorithms that detect errors in the received digital signal.
|
|
FDA:
Abbreviation for Food and Drug Administration. Organization responsible
for, among other things, laser safety.
|
|
|
FDDI:
Abbreviation for fiber distributed data interface. 1) A dual
counter-rotating
ring local area
network.
2) A connector used in a dual counter-rotating ring local area network
(illustrated).
|

|
|
FDM:
See frequency-division
multiplexing.
|
|
FEC:
See forward error correcting.
|
| Feeder:
1) Supplies the input of a system, subsystem, or equipment, such as a
transmission line or antennae. 2) A coupling device between an antennae
and its transmission line. 3) A transmission facility between either the
point of origin of the signal or at the head-end of a distribution
facility. |
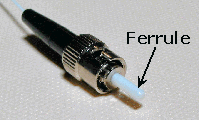
| Ferrule:
A rigid tube that confines or holds a fiber as
part of a connector
assembly. |
|
| FET:
Abbreviation for field-effect transistor. A
semiconductor so named because a weak electrical signal coming in
through one electrode creates an electrical field through the rest of
the transistor. This field flips from positive to negative when the
incoming signal does, and controls a second current traveling through
the rest of the transistor. The field modulates the second current to
mimic the first one, but it can be substantially larger. |
|
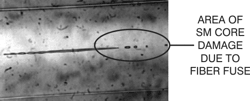
Fiber Fuse: A mechanism whereby
the core of a
single-mode fiber
can be destroyed at high optical power levels.
(Photo
courtesy of Dr. D.D.Davis.)
|
 |
| Fiber Grating:
An optical fiber in which the refractive index of the core varies
periodically along its length, scattering light in a way similar to a
diffraction grating, and transmitting or reflecting certain wavelengths
selectively. In its simplest form, a diffraction grating is little more
than a surface with repetitive lines that cause constructive and
destructive interference of light. |

|
|
Fiber-in-the-loop
(FITL):
Fiber optic service to a node that is located in a
neighborhood. |
| Fiber
Optic Attenuator:
A
component installed in a fiber optic transmission system that reduces
the power in the optical signal. It is often used to limit the optical
power received by the
photodetector
to within the limits of the optical receiver. A fiber optic attenuator
may be an external device, separate from the receiver, or incorporated
into the receiver design as illustrated (far left). |
 |
| Fiber Optic
Cable:
A cable containing one or more
optical fibers. |
| Fiber Optic
Communication System:
The
transfer of modulated or unmodulated optical energy through optical
fiber media which terminates in the same or different media. |
|
Fiber Optic Link:
A
transmitter,
receiver,
and
cable assembly
that can transmit information between two points. |
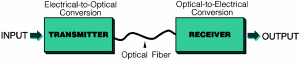 |
| Fiber Optic
Span:
An
optical fiber/cable
terminated at both ends which may include devices that add, subtract, or
attenuate optical signals.
|
Fiber Optic Subsystem:
A functional entity with defined bounds and interfaces which is part of
a system. It contains solid state and/or other components and is
specified as a subsystem for the purpose of trade and commerce.
|
|
Fiber-to-the-Curb
(FTTC):
Fiber optic service
to a node connected by wires to several nearby homes, typically on a
block. |
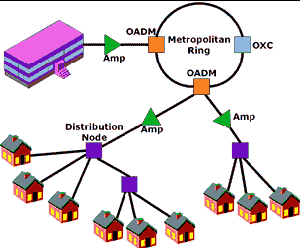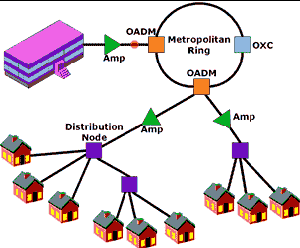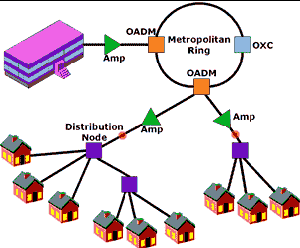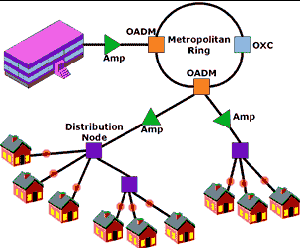
|
|
Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH):
Fiber optic service to a node located inside an individual home. |
| Fibre Channel:
An
industry-standard specification that originated in Great Britain which
details computer channel communications over fiber optics at
transmission speeds from 132 Mb/s to 1062.5 Mb/s at distances of up to
10 kilometers. |
| Filter:
A device which transmits only part of the incident energy and may
thereby change the spectral distribution of energy. |
|
| FIT Rate:
Number of device failures in one billion device hours. |
| Fluoride
Glasses:
Materials that have the amorphous structure of glass but are made of
fluoride compounds (e.g., zirconium fluoride) rather than oxide
compounds (e.g., silica). Suitable for very long wavelength
transmission. This material tends to be destroyed by water, limiting its
use. |
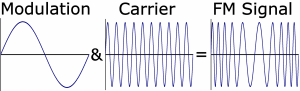
| FM (Frequency Modulation):
A method of
transmission in which the carrier frequency varies in accordance with
the signal. |
|
|
Forward Error Correcting (FEC):
A communication technique used to compensate for a noisy transmission
channel. Extra information is sent along with the primary data payload
to correct for errors that occur in transmission. |

|
| FOTP (Fiber Optic Test
Procedure):
Standards developed and published by the Electronic
Industries Association (EIA)
under the EIA-RS-455 series of standards. |
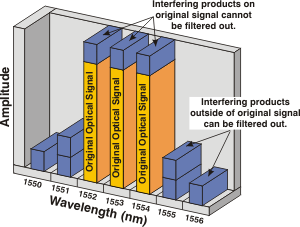
| Four Wave Mixing
(FWM):
A
nonlinearity
common in
DWDM
systems where multiple wavelengths mix together to form new wavelengths,
called interfering products. Interfering products that fall on the
original signal wavelength become mixed with the signal, mudding the
signal, and causing attenuation. Interfering products on either side of
the original wavelength can be filtered out. FWM is most prevalent near
the
zero-dispersion wavelength
and at close wavelength spacings. |
|
| FP:
Abbreviation for Fabry-Perot. Generally refers to any device, such as a
type of laser diode,
that uses mirrors in an internal cavity to produce multiple reflections.
|
| Free-Space Optics:
Also called free-space photonics. The transmission of modulated visible
or
infrared
(IR) beams through the atmosphere via
lasers,
LEDs,
or
IR-emitting diodes
(IREDs) to obtain broadband communications. |
| Frequency-division
Multiplexing
(FDM):
A method of deriving
two or more simultaneous, continuous channels from a transmission medium
by assigning separate portions of the available frequency spectrum to
each of the individual channels.
|
|
Frequency-shift Keying (FSK):
Frequency modulation
in which the modulating signal shifts the output frequency between
predetermined values. Also called frequency-shift modulation,
frequency-shift signaling. |
| Frequency Stacking:
The process that allows two identical frequency bands to be sent over a
single cable
by up converting one of the frequencies and "stacking" it with the
other. |
|
Fresnel Reflection Loss:
Reflection losses at the ends of fibers caused by differences in the
refractive index
between glass and air. The maximum reflection caused by a perpendicular
air-glass interface is about 4% or about -14 dB. |
|
FSAN: Abbreviation for full
service access network. A forum for the world’s largest
telecommunications services providers and equipment suppliers to work
define broadband access networks based primarily on the ATM passive
optical network structure.
|
http://www.fsanet.net/ |
|
Full-duplex
Transmission:
Simultaneous bidirectional
transfer of data. |

|
| Fused Coupler:
A method of making a multimode or single-mode coupler
by wrapping fibers together, heating them, and pulling them to form a
central unified mass so that light on any input fiber is coupled to all
output fibers. |

|
| Fused Fiber:
A bundle of fibers fused together so they maintain a fixed
alignment with respect to each other in a rigid rod. |
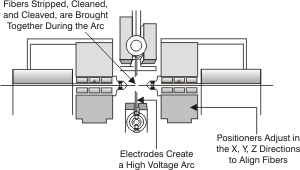
| Fusion Splicer:
An instrument that permanently bonds two fibers together by heating and
fusing them. |
|
| FUT:
Abbreviation for fiber under test. Refers to the fiber
being measured by some type of test equipment. |
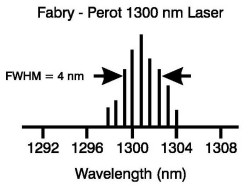
| FWHM:
Abbreviation for full width half maximum. Used to describe the width of
a spectral emission at the 50% amplitude points. Also known as FWHP
(Full Width Half Power) |
|
| FWM:See four wave
mixing. |